ENSURING PROJECT TEAM AND RESOURCES
# Not Relevant For Teachers
 INTRODUCTORY
INTRODUCTORY
” You should look at this section if you have only a limited idea of the project team and resources required for large scale assessment.”
Implementing large scale assessment requires a large amount of resources. These include financial resources, skilled human resources and infrastructure. Without the right resources in place, it will be difficult to achieve assessment quality and efficiency.
Ideally, each large scale assessment is run by an assessment centre or cell which includes people with all of the necessary skills and knowledge.This centre or cell might be located in a government department, university or research centre.
Key skills that are required in an assessment centre include:
- Project management–assessment programmes require a lot of coordination and complex procedures and these all need to be carefully managed;
- Test developers–the people responsible for developing assessment materials need to have relevant experience and training to do so;
- Language experts–the assessment materials need to be checked to make sure that the language is appropriate for students and/or to check translations (if any);
- Sampling experts–the people responsible for designing and implementing a sampling plan need to have specialised skills in sampling techniques;
- Fieldwork coordinators–the fieldwork for assessment programmes can be very complex and needs particular coordination;
- Data analysts–the people responsible for analysing and reporting assessment data need to have relevant skills and knowledge in data analysis; and
- Communications specialists–developing reports and disseminating information to different groups of stakeholders requires people with specific skills in communication
The number of people in each role will depend on the size of the education system. In a small state or province it might be enough to have a small team but in larger education systems a large team will be required.
It is common for assessment centres to include people who are only brought in to undertake particular activities such as test development. If they are well trained then this can be effective but the skills required to develop and implement assessment programmes are very specialised and need to grow over time. This means that it is beneficial to have people permanently allocated to an assessment centre so that they can build their expertise, and also to avoid them being taken away for other work.
It is important to realise that all of the assessment activities depend on others being completed. For example, test forms cannot be prepared and printed until assessment development is complete. This means that careful project management is required to ensure that all assessment activities happen according to their place in the schedule.
The choice of physical resources relates to decisions about assessment design. Is it delivered on paper and pen or on computer or tablet? Will data be manually entered or will Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) sheets be used and scanned? Will results be displayed on a website or will printed reports be created?
All of these questions have important consequences for cost and also for resources used.Another important consideration is accuracy. The more manual processes are used, the greater the possibility of error. And the more error, the less accurate assessment results will be. All of these matters need to be carefully considered in the planning phase.To find out more about project teams and resources, go to #Intermediate.
 INTERMEDIATE
INTERMEDIATE
” You should look at this section if you already know something about project teams and resources but would like to know more details. “
 To implement a large scale assessment it is necessary to have a strong team of staff with relevant skills in place, and the team also needs to follow robust project management principles, and to allocate enough time for all components of the project.The team should be comprised of a number of key roles:
To implement a large scale assessment it is necessary to have a strong team of staff with relevant skills in place, and the team also needs to follow robust project management principles, and to allocate enough time for all components of the project.The team should be comprised of a number of key roles:
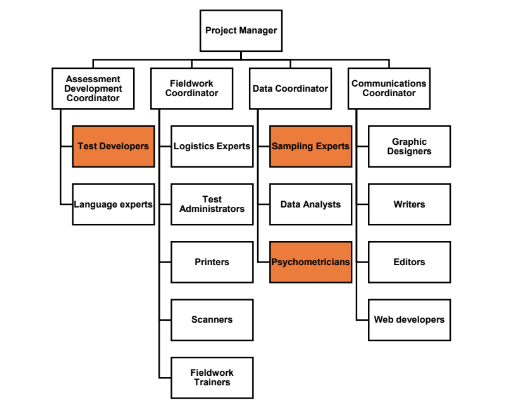
Some of these roles can be undertaken by professionals who are able apply their general skills to large scale assessment, such as graphic designers, language experts, printers and web developers.But some of these roles require very specific skills and / or expertise that can be difficult to find. This includes the three roles highlighted in the diagram–test developers, sampling experts and psychometricians.
It is essential that everyone given the role of test development, sampling or psychometric analysis has received specialised training in the skills and knowledge that they need. This can take many years of training. For example a psychometrician would be expected to have a PhD in statistics or psychology and a number of years of specialised training after that.
If advanced skills are not available, it is advisable to seek training and input from assessment experts to ensure that an assessment programme is rigorous and robust. This support may be required for several years before the local team is sufficiently skilled to run the assessment programme independently.
Beyond staff, another key consideration for large scale assessment is infrastructure. IT is increasingly common for large scale assessment to be done on computers or tablets as this enables better efficiency, accuracy and (when relevant) security.The use of computers does not make assessment high quality, however. Poor quality assessment on a computer is still poor quality assessment, and will not be able to collect accurate data on student learning. It is more important to focus resources on developing and implementing a high quality assessment than on using new technology.To find out more about project teams and resources, go to #Advanced.
 ADVANCED
ADVANCED
” You should look at this section if you already know about the project teams and resources required for large scale assessment and are interested in more details. “
To collect accurate data on student learning, a learning assessment needs to be built on high quality project teams and resources.While there are many roles that need to be filled there are some particularly key skills that are required. It is important to note that many months of work will be required for each of these teams, in addition to the other roles. High quality assessment programmes cannot be rushed and often take 2 to 3 years in total:
Test Administration Coordination Team–the test administration coordination team is responsible for all of the logistical components involved in conducting large scale assessment. This includes:
- (Paper based testing) Printing test forms and quality assuring print quality is consistent, dispatching test forms to testing centres, ensuring security and organising their return;
- (Computer based testing) Ensuring that all IT resources meet stringent quality standards, are reliable, have been thoroughly tested, are available at all test centres and that there is technical support available when required;
- Developing test administration manual, training test administrators, scheduling test administration, quality assuring test administration; reporting on consistency of test administration; and
- (If paper-based testing) arranging scanning or data entry of test booklets and quality assuring scanning or test entry processes.
Test Development Team–the test development team is responsible for developing the assessment materials for all relevant subjects and all grade levels. This includes:
- Developing an assessment framework to anchor the development of all cognitive and contextual items;
- Developing cognitive and contextual items to map to the specifications defined in the assessment framework, in addition to codebooks;
- Working collaboratively to review, provide feedback on and quality assure all cognitive and contextual items;
- Undertaking cognitive testing of items with students who are representative of the broader student population;
- Developing paper-based test forms or computer materials for delivering the test to students during the pilot and main survey;
- Training and quality assuring markers in scoring of open response data; and
- Reviewing data on item functioning after the analysis of pilot data and making revisions to items and test forms as appropriate.
Sampling and Data Analysis Team–the sampling and data analysis team is responsible for all of the data-related elements of the assessment programme. This includes:
- Collecting and validating accurate sampling frame data;
- Designing a sampling plan, including stratification if required, drawing the sample and documenting all steps involved;
- Quality assuring data entry and/or scanning;
- Cleaning and validating data collected in the pilot and main survey;
- Analysing pilot data and making recommendations for item selection for the main survey;
- Undertaking scaling of data from the main survey, using Item Response Theory models where appropriate;
- Applying sample weights and constructing replicate weights; and
- Building the assessment database and performing statistical analysis.
About the guidance levels
